背景和需求
前几年物联网刚刚兴起的时候就对这个行业很有兴趣, 去年买过一个树莓派3B捯饬过一段时间, 也了解了一些关于硬件方面的基础知识. 如今5G网络、智能家居、可穿戴设备、VR/AR/MR也都有了长足的发展, 再有如今机器学习领域的加持, 个人认为这些都是未来最有前景的方向.
作为一个软件工程专业出身的纯软件码农, 物联网用到的很多嵌入式和硬件相关的技术涉足很少, 先从简单的开始, 一步一个脚印学习吧. 现在有一个需求场景: 最近出门有时候忘记关门, 想做一个自动检测门是否关闭并可以远程控制的设备, 不仅能够提醒我这个粗心的人关门, 还可以作为家庭安防的一个组件. 米家也有类似的产品, 比如这个.
架构设计
虽然现在做的是一个简单的门窗传感器, 但考虑到后面会扩展其他设备, 良好的架构非常重要. 之前做的详细设计比较多, 架构设计也是边学边做. 首先系统的基本组件有以下几个, 通过分析逐渐细化, 来得到系统的模块视图和部署视图.
- 智能设备: 像门窗传感器这样的硬件设备
- 移动端APP: 能够实时获取到智能设备的信息并进行控制管理
- 云端服务: 设备和移动端后台服务以及数据中心
- 局域网服务: 房屋内部无线网络的小中心, 比如智能音箱, 家庭机器人这样的设备, 计算能力很强, 能够在房屋内进行设备的控制管理及更高级的服务, 暂时还没有计划做这块.
质量属性分析
通过需求明确了门窗传感器的应用场景和功能需求, 可以根据这些应用场景中所需要的非功能需求去确定系统的质量属性, 下面一一分析各项质量属性, 再根据需要实现的质量属性优先级作为架构设计的参考.
- 可用性: 目前仅家庭内部使用, 可用性达到99%以上即可.
- 可扩展性: 后续扩展其他设备, 要求系统能够支持动态扩展硬件设备
- 性能: 系统对实时性有一定要求, 传感器检测到变化需500ms内响应; 远程获取数据或控制时, 服务器延时在100ms以内; APP或管理端页面的响应时间在500ms以内
- 安全性: 由于数据会通过服务器交互, 需要有基本的用户鉴权, 目前用户只有我一个暂时没有非常强烈的安全性需求
- 可测试性: 由于整个系统包括软件前后端以及嵌入式设备, 各部分都需要能够独立开发并独立调试
- 易用性: 移动端APP需要最低的学习成本和较美观易用的UI; 嵌入式设备由于目前没有电烙铁焊接, 还是基于模块引脚通过线路直连, 易用性一般
可见目前架构中需要实现的质量属性优先级从高到低排序是这样的: 可扩展性, 可用性, 易用性, 可测试性, 安全性, 性能. 在架构设计中需要关注的主要是可扩展性以及可用性. 在后面进行架构设计和详细设计时需要考虑. 比如为了实现可扩展性, 采用统一的通信协议和API; 为了实现较高的可用性, 服务端需要守护进程及多副本策略; 为了能在保障基本的通信安全, 采用非明文的传输协议等等.
领域模型分析
**领域驱动设计(DDD)**的概念已经提出很多年了, 能够应对大型系统无法想象的复杂度, 分而治之. 自己动手做智能家居, 正好是一个从零构建一个软硬件齐全, 涉及面广泛的”复杂”系统, 来亲自实践一下领域驱动设计.
在我对DDD浅显的认识中, DDD首先要做的事情是:
- 抛开软件开发的知识, 专注于业务领域, 把业务需求作为问题域, 分解为多个尽可能关联较少的子域.
- 识别出子域中的实体、值对象、领域服务、聚合根等构建业务领域的原子
- 将上面的业务领域模型对应到软件设计领域中, 并以此作为架构设计的参考
这些只是个人感悟, 并不一定是正确的, 但这样的设计思路是完全符合软件设计的几个原则的: 单一职责(SRP), 最小知识(LKP), 依赖倒置(DIP). 每个子域的实现也将会是高内聚的, 子域间的耦合也将比”大泥球”式的一起设计实现小很多. 下图是对智能家居系统子域简单的划分: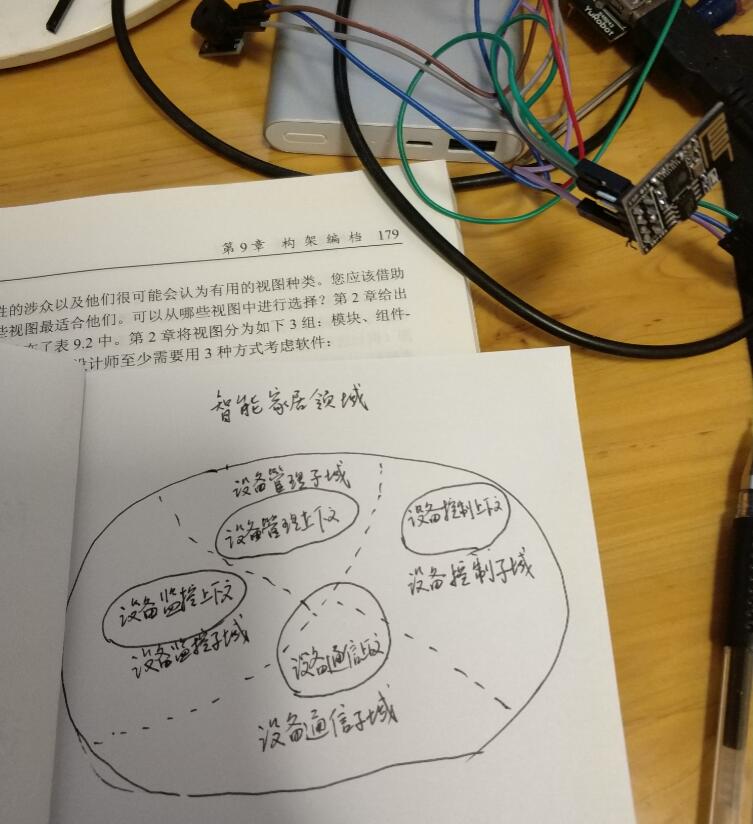
- 设备管理子域是核心子域, 包括对智能家居硬件设备的添加变更以及状态信息展示等管理业务, 通俗的说就是对设备及相关实体的增删改查
- 设备监控子域包括每个设备是否在线、是否正常的相关业务, 提供健康监测功能
- 设备控制子域包括了每个设备可用的控制指令, 以及设备之间的连锁控制相关的业务. 这个子域是一个复杂的状态机, 每个智能设备接受到某个指令或被动触发某个事件时, 如何响应, 状态如何变化等等. 这部分的设计是系统可扩展性和可修改性的关键.
- 设备通信子域是数据交换中心, 对于每个设备每种指令系统都有统一的原语去表示, 去传输. 这也是系统可扩展性的关键. 由于不同的智能家居设备差别极大, 设备与服务器, 设备与设备之间如何通信是很有挑战的, 比如使用适配层或代理模式等等.
通过子域的划分, 可以初步识别出业务领域存在这些实体:
- 设备基础信息
- 设备状态
- 通信消息
- 设备控制器
注: 由于设备的使用和事件处理应该是看得见并且可随时修改的, 对设备的控制逻辑以及事件处理链也应该是看得见的有标识的实体数据, 而不是以领域服务的形式存在于系统中, 这样才能使得可扩展性最大化.
逻辑架构
经过领域模型的分析, 服务端可以拆解为三个子应用服务和一个通用服务, 分别是设备监控服务, 设备管理服务, 设备控制服务, 外加一个消息中心. 架构设计应该有多个静态和动态的视图通过不同的UML图来表示, 这里仅画了模块结构来体现系统的逻辑架构.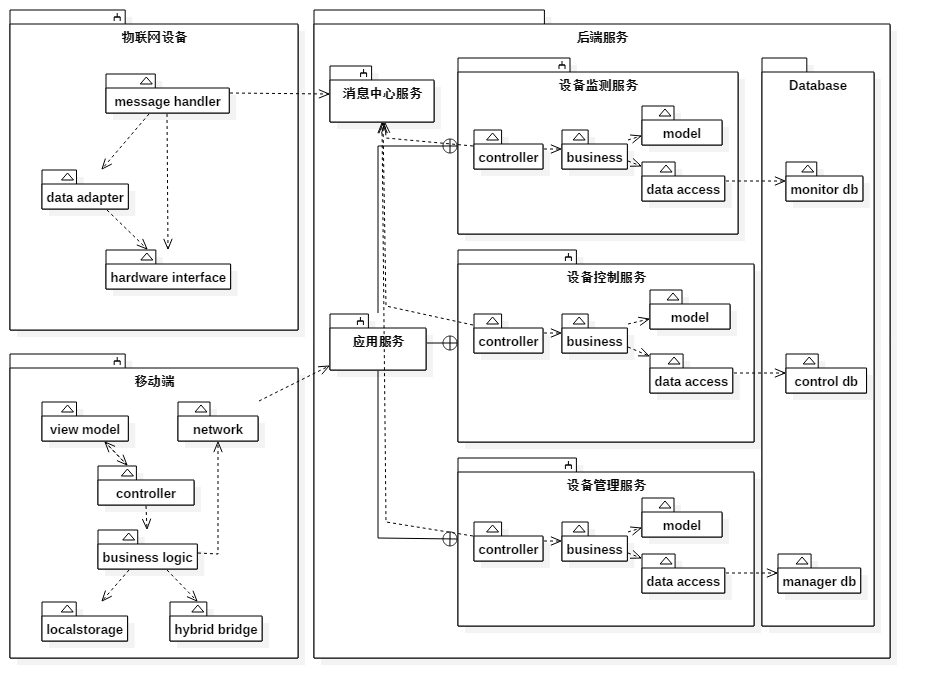
部署架构
通过领域分析和逻辑架构的梳理, 最终的部署架构应该是下图这样的: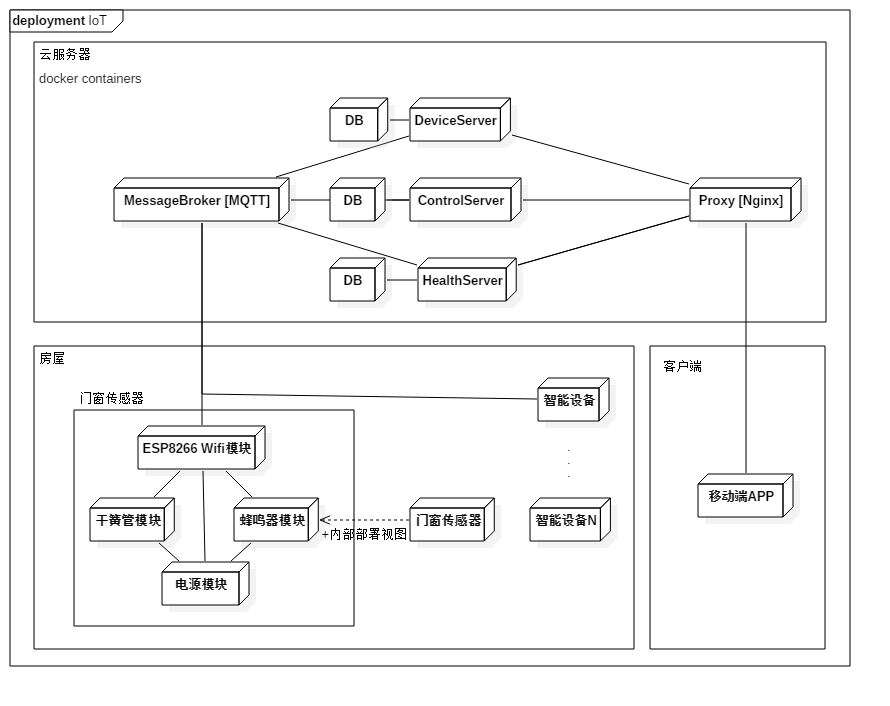
- 云端三个应用服务分别部署在不同的Docker容器中(由于我的服务器配置太烂没法上Kubernetes了)
- 不同的应用服务连接不同的MongoDB数据库(不同的MongoDB属于同一个Docker容器)
- 虚拟机上直接部署MQTT服务端作为设备通信中心
- 物联网设备通过家庭Wifi连接到中心消息服务
- 移动端通过Nginx反向代理与多个应用服务通信
技术选型
通信协议
整个系统的通信可以分为应用软件的通信与底层嵌入式设备的通信, 应用层无疑是采用REST风格的HTTP协议作为统一的通信方式, 但嵌入式设备的通信协议五花八门, 比如这里就列举了11种通信方式, 那如何选择合适的物联网通信协议呢? 我们分别对比一下常见通信协议的优劣势.
- 蓝牙: 2.4GHz频率/1Mbps速率/50~150米通信距离/低功耗
- ZigBee: 2.4GHz频率/0.25Mbps速率/10~100米通信距离/低功耗
- Wifi: 2.4GHz 5GHz频率/150~600Mbps/50米通信距离/高功耗
- 蜂窝网络: 900-1800-1900-2100MHz频率/35Kbps~10Mbps速率/有基站就有通信/中等偏高的功耗
常见的底层通信协议中, 米家的门窗传感器选择的是ZigBee协议, 我现在选择的是Wifi, 一方面因为功耗通过大容量电池可以解决, 另一方面通过Wifi可以复用基于TCP之上的无数应用层协议, 实现与高层应用服务直接打通, 减少通信数据适配层的开发量. 经过初步测算, ESP8266设置成station模式处于低功耗工作状态下电流约0.3mA, 两节5号电池大约3000mAh的容量, 大约可以使用1年. 但米家的产品采用ZigBee的低功耗通信, 一个240mAh的纽扣电池就可以用两年以上, 商用肯定Zigbee和蓝牙是正确的选择.
在Wifi之上, 数据传输格式相关协议也有很多选择, 比如嵌入式设备直接处理HTTP/HTTPs协议的数据, 32位mcu的ESP8266芯片处理是没有压力的, 但考虑到物联网世界与互联网的差别, 选择了更适合物联网应用场景的MQTT协议, 这里有MQTT的详细介绍, 它同样构建于TCP/IP之上, 但比HTTP小巧, 而且设计初衷就是一个Broker架构的消息发布-订阅框架, 非常适合物联网设备在网络不可靠情况下的全双工通信.
总结一下, 通信协议的技术选型是这样的:
- 移动端APP-服务器通信: HTTP协议, RESTful WebAPI, 另外使用WebSocket做全双工通信
- 设备-服务器通信: MQTT协议, 自定义数据格式
- 设备-设备通信(目前还没有): ZigBee协议- Wifi数据适配层 - MQTT协议
嵌入式设备
上面的部署视图已经暴露了硬件设备和芯片的选型:
- Wifi: ESP8266-01S
- 蜂鸣器: 无源蜂鸣器一枚
- 电源: 2节AA电池 / 5V充电宝+电源模块
- 传感器: 干簧管传感器一枚
其实一开始想做门窗传感器的时候, 想到的是超声波测距模块, 但看到米家的产品后发现原来还有干簧管这么神奇的东西, 外加一块永磁体就能判断距离了, 而且几乎是零功耗的.
服务端
应用服务部署在个人的阿里云ECS上, 为了更快的开发和更小的资源占用(买的最低端的ECS服务器只有1GB内存1核CPU), 以及更方便的WebSocket编程, 暂定使用Node.js全家桶. 服务端技术选型有:
- 基础设施: Docker容器
- 数据库: MongoDB
- 应用框架: Koa2
- 实时通信: socket.io
移动端APP
移动端开发并不是我擅长的领域, 目前业务逻辑不太复杂, 又有快速开发和跨平台的需求, 准备尝试一波Hybrid + Vue.js来做移动端App. Hybrid开发暂定用DCloud平台, 但不准备使用DCloud家的MUI, 因为如今的前端开发再不用MVVM就太不Geek了. 相比之下, Vue在移动端也有很多优秀的组件库, 比如:
- Mint UI 10.1k star, Element UI的移动端版本, 组件不多
- vux 12.1k star, 组件很多但无专职团队维护
- vonic 2.6k star / vant 2k star / Keen-UI 3.3k star
前端组件库中选择了MintUI, 整个移动端技术选型总结一下大概有这些:
- Hybrid框架: Dcloud
- 前端MVVM框架: Vue.js + Vuex
- 前端组件库和第三方库: MintUI, axios, socket.io, …
- 前端打包: Webpack
架构设计和技术选型搞定了, 下面就开始详细设计和撸代码了。